|
Chapter 1 Big Idea! How is place value used in our everyday life? |
|
| 1-1 | How do you use base ten blocks to make a twodigit number? |
| 1-2 | How does the place of a digit tell you the placevalue? |
| 1-3 | How does using logical reasoning help in solvingproblems? |
| 1-4 | How do you write numbers using words? |
| 1-5 | How do you estimate to find “how many”? |
| 1-6 | How do you use the number line to order numbers? |
| 1-7 | How do you compare numbers using <,>, or =? |
| 1-8 | How do you identify patterns and continue thepattern? |
| 1-9 | What clues help you choose a problem solvingstrategy? |
| 1-10 | What patterns do you see when you skip count? |
| Chapter 2 Big Idea!
How can you use addition to find out “how many”? |
|
| 2-1 | How do you know the sum will not change when youswitch the order of the addends? |
| 2-2 | How do you use the number line to count on? |
| 2-3 | How does acting out help in solving problems? |
| 2-4 | How do you think using doubles will help you solveaddition problems? |
| 2-5 | How can you use doubles to learn other addition facts? |
| 2-6 | How does making ten make it easier or harder to add? |
| 2-7 | How can you add numbers in different ways to simplifycolumn addition? |
| 2-8 | What clues help you choose a problem solving strategy? |
|
Chapter 3 Big Idea! How do you use subtraction in the real world? |
|
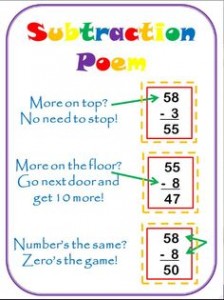
| 3-1 | How do you use the number line to subtract? |
| 3-2 | What happens when you subtract all or 0? |
| 3-3 | How do you use double facts to subtract? |
| 3-4 | How does guess and check help you with problemsolving? |
| 3-5 | How do you use addition to help you find the difference? |
| 3-6 | What makes addition and subtraction inverse operations? |
| 3-7 | How do fact families help in solving addition andsubtraction problems? |
| 3-8 | What clues help in deciding which operation to use tosolve a problem? |
|
Chapter 4 Big Idea! How can you show data collected from a survey? |
|
| 4-1 | How do tally marks help you organize data? |
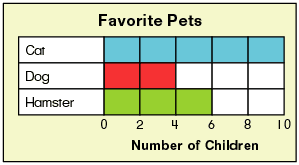
| 4-2 | How are picture graphs and tally charts different? |
| 4-3 | How do you use picture graphs to draw conclusions? |
| 4-4 | How does creating a table help solve problems? |
| 4-5 | How are bar graphs different from picture graphs? |
| 4-6 | How do you use bar graphs to draw conclusions? |
| 4-7 | How do you determine the probability of an event? |
| 4-8 | What clues help in deciding which operation to use tosolve a problem? |
|
Chapter 5 Big Idea! How does rounding numbers make addition easier in real world problems? |
|
| 5-1 | How is adding “tens” similar to adding basic facts? |
| 5-2 | Why is it important to learn how to count by 10’s? |
| 5-3 | How will working backward help solve multiplicationproblems? |
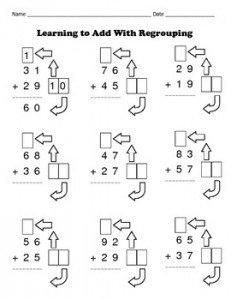
| 5-4 | How do you know if you have to regroup? |
| 5-5 | How do you show regrouping? |
| 5-6 | What steps do you follow when adding two digitnumbers? |
| 5-7 | How do you estimate sums? |
| 5-8 | How is adding 3 two digit numbers like adding 2 twodigit numbers? |
| 5-9 | What clues help you to choose a problem solving strategy? |
|
Chapter 6 Big Idea! How do we use subtraction in the real world? |
|
| 6-1 | How can you use single digit subtraction facts tosubtract 10’s.? |
| 6-2 | How do you use base 10 blocks to count back by tens? |
| 6-3 | Why do you sometimes have to regroup in order tosubtract? |
| 6-4 | How does writing a number sentence help whensolving problems? |
| 6-5 | When do you need to regroup in order to subtract? |
| 6-6 | What steps do you follow when regrouping forsubtraction? |
| 6-7 | Why does addition work as a check for subtraction? |
| 6-8 | What clues help you to choose a problem solvingstrategy? |
| 6-9 | How can rounding help when estimating the difference? |
|
Chapter 7 Big Idea! Why is it important to know the value of each coin and be able to add them? |
|
| 7-1 | How is the cent symbol used to name the value of coins? |
| 7-2 | How do you order coins in order to count them? |
| 7-3 | Why is it helpful to put coins in order before countingthem? |
| 7-4 | How does “Acting It Out” help to solve problems? |
| 7-5 | How are dollar and cent signs different and alike? |
| 7-6 | How is adding money different than adding two digitnumbers? |
| 7-7 | How is subtracting money subtracting other two digitnumbers? |
| 7-8 | What clues help you to determine the best strategy forproblem solving? |
|
Chapter 8 Big Idea! Why is it important to understand temperature and time? |
|
| 8-1 | How do you read a thermometer? |
| 8-2 | How do you compare units of time measurement? |
| 8-3 | How do you tell time to the hour and the half hour? |
| 8-4 | How does it help to find a pattern in problem solving? |
| 8-5 | How do you use the minute hand to tell time to thequarter hour? |
| 8-6 | How do you skip count by 5’s to tell time? |
| 8-7 | Why would someone want to collect temperature data? |
| 8-8 | What clues help you to determine the best strategy forproblem solving? |
|
Chapter 9 Big Idea! How do fractions help us do ordinary things everyday? |
|
| 9-1 | How are unit fractions alike? |
| 9-2 | How are the fractions ¼ and 2/8 alike? |
| 9-3 | How does drawing a picture help in problem solving? |
| 9-4 | Why does a fraction for the whole have the same numberon the top and bottom? |
| 9-5 | How do you know if a fraction is closer to 0, ½, or 1? |
| 9-6 | What does the fraction ¼ of a group mean? |
| 9-7 | How would you use a fraction to show part of a group? |
| 9-8 | What clues help you to determine the best strategy forproblem solving? |
|
Chapter 10 Big Idea! How would understanding place value help in estimating numbers up to one thousand? |
|
| 10-1 | How would you show 3 digit numbers using base tenblocks? |
| 10-2 | How do you use a place value chart to identify valuesof 3 digit numbers? |
| 10-3 | How can making a list help you solve problems? |
| 10-4 | How do you write a number in expanded form from amodel? |
| 10-5 | How do you read and write numbers to one thousand? |
| 10-6 | What clues help you to determine the best strategy forproblem solving? |
| 10-7 | How do you compare numbers using < , = , > ? |
| 10-8 | How do you use place value to order numbers? |
| 10-9 | How can you tell if the number pattern is countingby 100’s? |
| Chapter 11 Big Idea!
Where do you see 2 and 3-dimensional figures in the real world? |
|
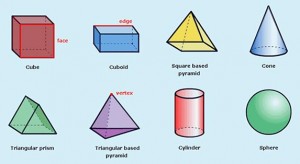
| 11-1 | What are three dimensional figures? |
| 11-2 | How can you describe three dimensional figures? |
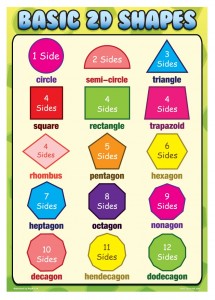
| 11-3 | How can you identify a 2-dimensional figure? |
| 11-4 | How does looking for a pattern help in problem solving? |
| 11-5 | How does the number of sides & vertices determine a2 dimensional figure? |
| 11-6 | How do you compare figures? |
| 11-7 | How can you combine figures to form new figures? |
| 11-8 | What clues help you to determine the best strategy forproblem solving? |
| 11-9 | How do you find a point on a number line? |
| 11-10 | How do you locate points on a grid? |
|
Chapter 12 Big Idea! How do you use non-standard and standard units of measure? |
|
| 12-1 | How do you measure objects with nonstandard unitsof measure? |
| 12-2 | Why is it better to measure in inches, rather thanpaperclips? |
| 12-3 | How does guess and check help in solving problems? |
| 12-4 | How would you use a ruler to measure in inches? |
| 12-5 | How do you measure objects using metric measurement? |
| 12-6 | How do you estimate using metric measurement? |
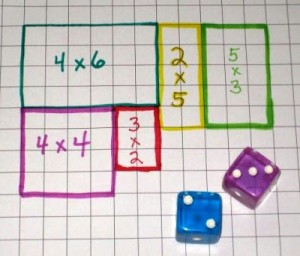
| 12-7 | How do you determine the area using pattern blocks? |
| 12-8 | What clues help you to determine the best strategy forproblem solving? |
|
Chapter 13 Big Idea! How do we use measurement in everyday life? |
|
| 13-1 | How can you use nonstandard units to measure capacity? |
| 13-2 | What is the difference between the amount a cup can holdand the amount a gallon can hold? |
| 13-3 | How can acting it out help to solve a problem? |
| 13-4 | How can we estimate capacity using milliliters and liters? |
| 13-5 | How do we use nonstandard units to measure weight? |
| 13-6 | What is the difference between ounces and pounds? |
| 13-7 | What is the difference between a gram and kilogram? |
| 13-8 | What are the clues to help you solve the problem? |
| Chapter 14 Big Idea!
Why is knowing addition and subtraction facts helpful in the real world? |
|
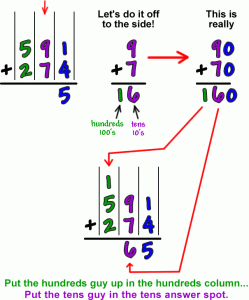
| 14-1 | How can you add numbers in the hundreds? |
| 14-2 | How is three digit addition like two digit addition? |
| 14-3 | How is regrouping ones different from regrouping tens? |
| 14-4 | How does making a table help in problem solving? |
| 14-5 | When do you estimate? |
| 14-6 | Why can you use single-digit number facts to subtracthundreds? |
| 14-7 | How is subtracting 3-digit numbers like subtracting2-digit numbers? |
| 14-8 | How do you know when to regroup? |
| 14-9 | Why is it important to know how to round andestimate? |
| 14-10 | What clues help you to solve the problems? |
|
Chapter 15 Big Idea! How can the making of models help us to understand the world around us? |
|
| 15-1 | How can making models for word problems help usunderstand the problem? |
| 15-2 | How can skip counting help you find the total when thereare equal groups? |
| 15-3 | How can drawing a picture help you solve theproblem? |
| 15-4 | How does repeated addition help you understandmultiplication? |
| 15-5 | How can arrays help you multiply? |
| 15-6 | What can you do to share things equally? |
| 15-7 | What can you do to make equal groups? |
| 15-8 | What clues help you solve the problem? |