Chapter 1-Using Place Values to 100 and Patterns
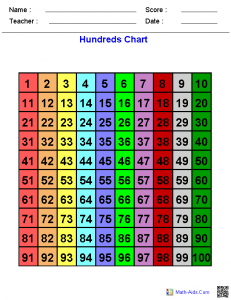
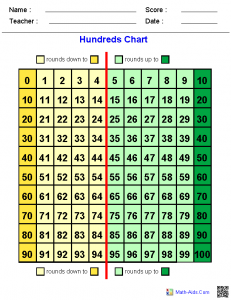
Hundreds Chart– Click to enlarge
Summary
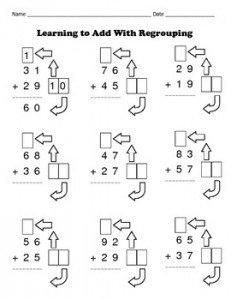
1-1 Tens and Ones: I can count, read, and write tens and ones.
Vocabulary: Ones: a place value of a number. Example: In the number 23, the 3 is in the ones place. This number has 3 ones. Tens: a place value of a number. Example: In the number 23, the 2 is in the tens place. This number has 2 tens.
1-2 Place Value to 100: I can use models of tens and ones to show numbers to 100.
Vocabulary: Digit: a symbol use to write numbers (there are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and, 9). Place Value: value given to a digit by its place in a number. For example, in the number 46, the 4 is in the tens place… so it isn’t just a 4… it is 4 tens which means it has the value of 40.

Place Value Chart– Click to Enlarge
1-3 Use Logical Reasoning: I can use logical reasoning to solve problems.
1-4 Read and Write Numbers: I can read and write numbers to 100.
1-5 Estimate Amounts: I can estimate amounts to 100.
Vocabulary: Estimate: finding a number close to an exact amount.
1-6 Order Numbers: I can order numbers to 100.
Vocabulary: Number line: a line with numbers on it often used in math. Before: on a number line (5,6,7) 6 is before 7. After: to follow in place or time. Between: on a number line, (48, 49, 50) 49 is between 48 and 50.
1-7 Compare Numbers: I can compare numbers to 100.
Vocabulary: Compare: seeing how numbers are alike and different. Is greater than >: the number on the left side of the symbol is greater or larger than the number on the right. Is less than <: the number on the left side of the symbol is less than or smaller than the number on the right. Is equal to =: both numbers have the same value on either side of the symbol.
1-8 Patterns: I can create and use patterns to solve problems.
Vocabulary: Pattern: is an order that a set of objects or numbers follows over and over or how a set grows.
1-9 Choose a strategy: I can choose the best strategy to solve a problem.
1-10 Patterns on a Hundred Chart: I can create and use patterns on a hundred chart to solve problems.
Vocabulary: Skip Count: counting objects in equal groups or multiples of two or more.